Understand the purpose of a medical device quality management system (MD-QMS), interaction with appropriate medical device regulatory authority requirements, quality management systems standards, third-party certification, and the business benefits of the quality management system.
Understand the role and responsibilities of an auditor to plan, conduct, report, and follow-up a quality management system audit in accordance with ISO 19011 and ISO/IEC 17021
Learn to plan, conduct, report, and follow-up an audit of a medical device quality management system to establish conformity (or otherwise) with ISO 13485 and applicable medical device regulatory requirement documents in accordance with ISO 19011, ISO/IEC 17021.
ISO 13485:2016 is applicable to organizations involved in the medical device industry. Here are some specific contexts where it is relevant:
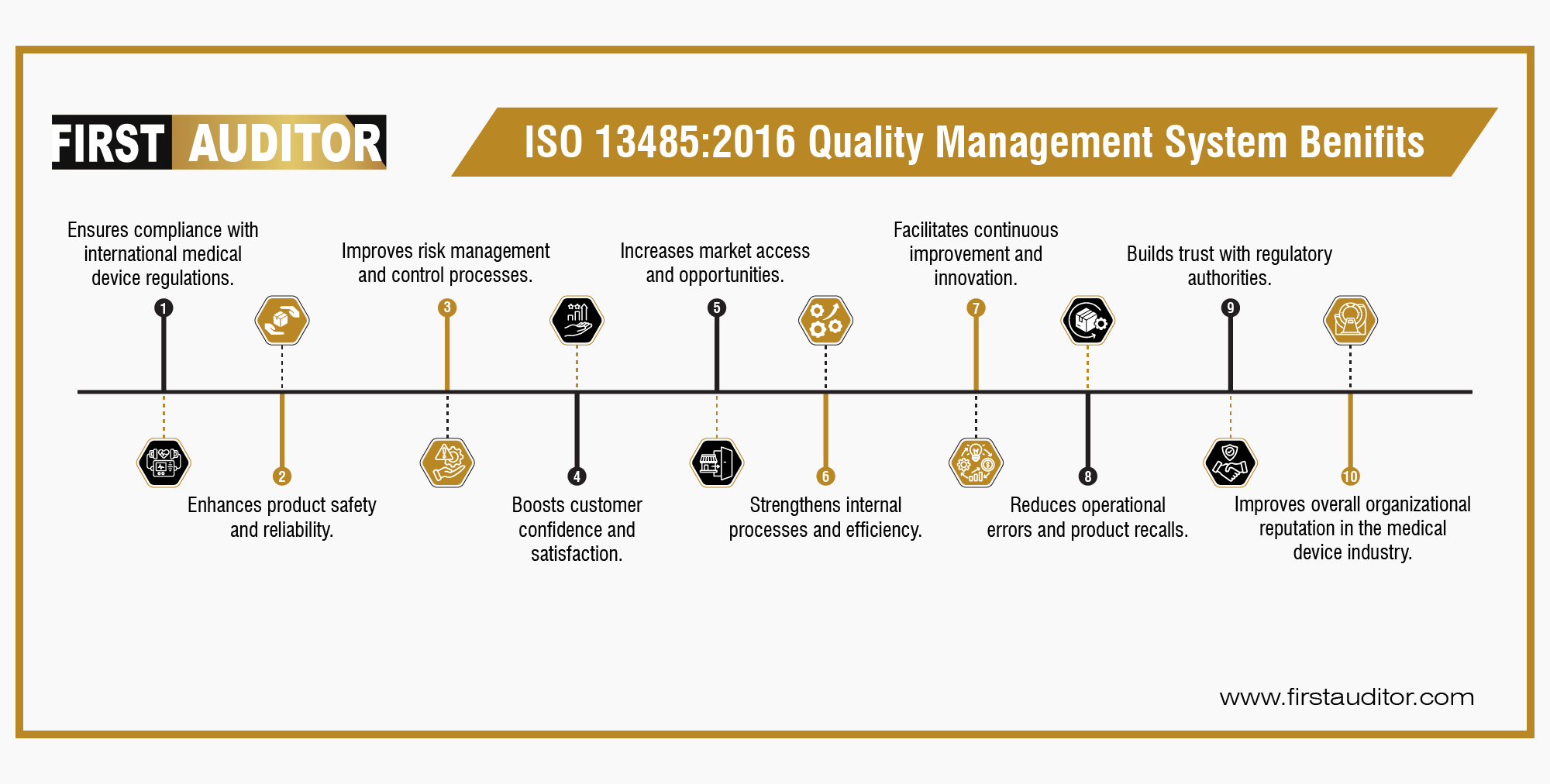
ISO 13485:2016 is an international standard for quality management systems specifically tailored for the medical device industry. It outlines the requirements for a QMS to ensure that medical devices consistently meet regulatory and customer requirements.
ISO 13485:2016 is applicable to organizations involved in the design, development, production, installation, and servicing of medical devices. This includes manufacturers, distributors, service providers, and regulatory bodies.
The time frame varies depending on the size and complexity of the organization, but typically it can take between 6 to 12 months from initial preparation to certification.
ISO 13485:2016 is specific to the medical device industry and includes additional requirements for regulatory compliance and risk management. ISO 9001:2015 is a general quality management standard applicable to a wider range of industries.
The key requirements include establishing a documented QMS, implementing risk management processes, maintaining design and development controls, ensuring traceability, managing non-conformities, and conducting internal audits and management reviews.